| CAS
NO. |
80-51-3 |
|
| EINECS
NO. |
201-286-1 |
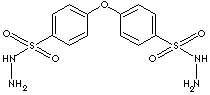
| FORMULA |
O(C6H4SO2NHNH2)2 |
| MOL
WT. |
358.39 |
| H.S.
CODE |
2935.00.9090 |
| TOXICITY |
|
| SYNONYMS |
p,p'-Oxybisbenzenesulphonyl hydrazide;
|
| Benzenesulfonic acid, 4,4'-oxybis-, dihydrazide;
4,4'-氧双(苯磺酰肼)
(Chinese); 4,4'-Oxybis(benzenesulfonyl)hydrazide; 4,4'-Oxydi(benzenesulphonohydrazide); Diphenyloxide 4,4'-sulphonylhydrazide; 4,4'-Oxydi(benzolsulfonohydrazid) (German); 4,4'-oxidi(bencenosulfonohidrazida)
(Spanish); 4,4'-oxydi(benzenesulfonohydrazide) (French); |
| PRICE |
|
| CLASSIFICATION
|
|
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
|
| PHYSICAL
STATE |
white crystalline powder |
| MELTING POINT |
130
C |
| BOILING
POINT |
140
C (Decomposes) |
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY |
1.52 |
| SOLUBILITY
IN WATER |
insoluble |
| AUTOIGNITION |
|
| pH |
|
| VAPOR DENSITY |
|
| NFPA RATINGS |
|
|
REFRACTIVE
INDEX
|
|
| FLASH
POINT |
|
| STABILITY |
Stable under ordinary conditions. Oxidizes in light |
|
APPLICATIONS
|
|
Hydrazine (anhydrous) is a clear, fuming, corrosive liquid with an ammonia-like
odor; melting at 1.4 C, boiling at 113.5 C, specific gravity 1.011. It is very
soluble in water and soluble in alcohol. It decomposes on heating or exposure to
UV to form ammonia, hydrogen, and nitrogen, which may be explosive with a blue
flame when catalysed by metal oxides and some metals such as platinum or Raney
nickel. It is prepared from ammonia with chloramine in the presence of glue or
gelatin (to inhibit decomposition of the hydrazine by unreacted oxidants) as the
hydrate form usually (100% monohydrate contains 64% by weight hydrazine).
Hydrazine is also prepared from sodium hypochlorite with urea in the presence of
glue or gelatin. Botht ammonia and amines are nitrogen nucleophiles which
donate electrons (they are Lewis bases). But hydrazine (diamine) has much
stronger nucleophilicity which makes it more reactive than ammonia. Hydrazine
has dibasic and very reactive properties. Hydrazine is used as a component in
jet fuels because it produce a large amount of heat when burned. Hydrazine is
used as rocket fuel. Hydrazine is used as an oxygen scavenger for water boiler
feed and heating systems to prevent corrosion damage. Hydrazine is used as a
reducing agent for the recovery of precious metals. It is used as a
polymerization catalyst and a chain extender in urethane coatings. It and its
derivatives are versatile intermediates. They have active applications in
organic synthesis for agrochemicals, pharmaceuticals, photographic, heat
stabilizers, polymerization catalysts, flame-retardants, blowing agents for
plastics, explosives, and dyes. Recently, hydrazine is applied to LCD (liquid
crystal displays) as the fuel to make faster thin-film transistors. Hydrazide is an acyl hydrazine. Acyl (-CO) is an organic radical formed by
removal of a hydroxyl group from an organic acid (carboxyl group). p,p'-Oxybisbenzenesulphonyl hydrazide
is a Chemical Blowing agents for cellular plastic,
rubbers, PVC
plastisol, and CR foams. |
| SALES
SPECIFICATION |
|
APPEARANCE
|
white powder |
| DECOMPOSITION
TEMP |
140
- 160 C
|
|
GAS
YIELD |
110
min (ml/g)
|
|
PARTICLE
SIZE
|
80
% min (>15 µm)
|
| TRANSPORTATION |
| PACKING |
25kg
sin bag |
| HAZARD CLASS |
|
| UN
NO. |
|
| DESCRIPTION
OF BLOWING AGENT |
|
Blowing agents, also called Foaming agents, can
be classified as Physical and Chemical Blowing Agents. Physical
blowing agents are not under chemical changes during processing.
Physical blowing agents are in forms of liquid or compressed
gas which will transfer state into gases or low boiling
liquid during processing causing resins into cellular structure.
Chemical Blowing Agents are mainly solid form of hydrazine
derivatives include Azodicarbonamide;
p,p'-Oxybis(benzenesulfonyl hydrazide); 5-Phenyltetrazole;
p-Toluene sulfonyl semicarbazide;
Trihydrazine Triazine; They commonly release gases such
as nitrogen, carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide or ammonia.
But ammonia is not desirable as it effects on degrade of
resins. There are nonazo blowing agents releasing carbon
dioxide such as sodium borohydride.
Blowing
Agent Class
- Azo
Compounds
- Azodicarbonamide
(CAS RN: 123-77-3)
- Hydrazine
Compounds
- p-Toluenesulfonylhydrazide
(CAS RN: 1576-35-8)
- p,p'-Oxybis
(Benzenesulfonylhydrazide) (CAS RN: 80-51-3)
- Benzenesulfonyl Hydrazide
(CAS RN: 80-17-1)
- p-Toluenesulfonyl acetone hydrazone
- Carbazides
- p-Toluenesulfonylsemicarbazide
(CAS RN: 10396-10-18)
- p,p'-Oxybis
(Benzenesulfonylsemicarbazide)
- Tetrazoles
- 5-Phenyltetrazole
(CAS RN: 18039-42-4)
- Nitroso
Compounds
- N,N’-Dinitroso-pentamethylenetetramine
(CAS RN: 101-25-7)
- Carbonates
- Sodium
Bicarbonate (CAS RN: 144-55-8)
|
